
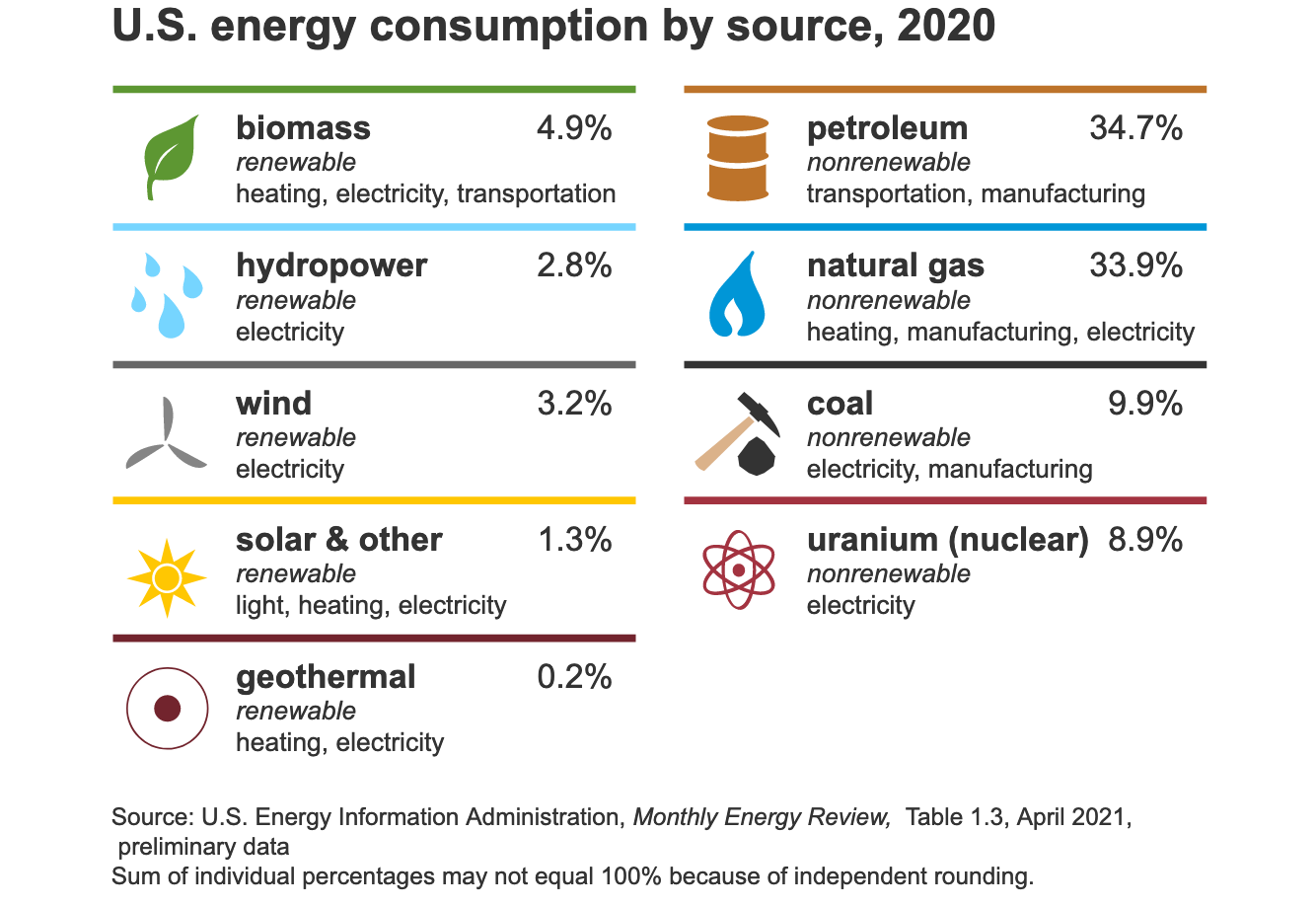
Renewable energy sources can be defined as any source that produces electricity and other useful forms without the use of fossil fuels or polluting resources. These sources include biomass, hydroelectricity solar and geothermal. These technologies are likely to play a significant role in the global movement for climate change.
The fastest-growing sources of electricity in America and the world are solar and wind. These technologies are expected continue to grow globally. Wind resources are particularly abundant in the Appalachian Mountains and the Great Plains. Photovoltaics are the fastest growing type of solar technology and will add 139 GW of global capacity by 2020. These technologies are capable of providing electricity as well as low-temperature heat and water heating.
Biomass has been used as a fuel for cooking and heating for thousands of year. Biomass can be made from plant residues, agricultural waste and forest byproducts. It can also be fermented for hydrogen and biodiesel.
For many years, hydropower has been used. The power of water flowing in rivers is one source of electricity that has been around for a long time. Historically, it has been a reliable supply source. Relying on renewables is not without its problems.
Grid integration of these technologies is difficult because of the intermittent nature. This is especially true at higher levels of deployment. As variable renewables become more prevalent, so do system costs.
Although solar and wind are relatively easy to utilize, it can be difficult to integrate these technologies into a grid. This is because backup generation capacity is necessary. The amount of sunlight available can also be affected by the weather and the time of day. Also, efficiency and cost can impact the amount of energy used.
By 2020, wind and solar power will account for 29 percent of global electricity generation. These technologies will see an increase in use, which will result in a reduction of carbon dioxide emissions, and a smaller global carbon footprint.
Geothermal energy has been used for heat since ancient times. This energy source is used for space heating by the Romans. However, most people are unable to access it today. Enhanced geothermal systems use advanced drilling techniques and fluid injection to access this resource.
The most common form of biomass is wood. It can come from trees, plant material, or municipal solids. Wood can be turned into biofuels like alcohol. Direct heating can be done with domestic hot water units.
A number of countries are utilizing these resources. China and India, in fact, have pledged to build 78GWE of capacity by 2030. This would allow for a 9% drop in per capita CO2 emission. Germany is currently home to some of the most powerful power-to-gas plants, including a 6MW unit at Energiepark Mainz and an Element Eins unit that are both 20 MW.
FAQ
What impact does climate change have on food security and agriculture?
Climate change, global warming, and other factors have direct impacts on agriculture and food supply. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can impact farming activities, reduce crop yields, or cause loss of agricultural diversity. Warmer temperatures can cause crop diseases and pests to multiply. It can also affect the ranges that are suitable for agricultural production. In turn, this could increase the cost of food production and result in a greater incidence of hunger and poor nutrition worldwide.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. The changing climate has a similar effect on livestock production. High summer temperatures can decrease the fertility rates of animals like goats, sheep, cattle, and sheep. This can in turn lead to lower milk yields, which can increase food security across communities.
The relationship between climate change and global warming is a complex one; however, efforts are being made to mitigate these results through adaptation strategies implemented by governments worldwide such as strategic investments in climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This means promoting sustainable methods, such as crop rotation and the preservation of native seed varieties. These strategies help prevent adverse effects from climate change or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
What are the effects of climate change on the environment and society?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change has many environmental effects. These include rising global temperatures, increased extreme weather events and sea level rise. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
Global climate change has one of the most powerful effects on ocean levels. This results in shoreline erosion on many coasts, as well as increased flooding risk for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events cause massive destruction to homes, businesses, and sometimes even wipe out entire towns. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
These dramatic changes in living conditions can often lead to displacement and even refugee crisis when people leave their homes voluntarily or involuntarily due to their changing climate.
People with respiratory diseases such as asthma are particularly vulnerable to dust storms from increased aridity. Additionally, pest infestations are likely to rise significantly in conjunction with higher temperature extremes (a phenomenon known as the "greenhouse bug") which can cause further damage to agricultural production. This could further affect global food security numbers. As fewer crops become available at poorer nutritional qualities, it may bring additional hardships on marginalized communities already struggling to make ends meets otherwise.
What are the impact of deforestation and land use change on climate change?
The climate can be directly affected by deforestation and changes in land use. Carbon dioxide, which is the most important greenhouse gas on Earth, can't be absorbed by trees if they are removed or burned. The atmosphere is less carbon dioxide if trees are removed by deforestation, or burned for agriculture purposes.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Clearance can increase exposure of soils that have large amounts stored carbon. These soils release carbon dioxide when they are turned over or disturbed through farming activities.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. For instance, smoke from burning events associated with deforestation has been linked to decreased visibility as well as health concerns such as asthma and other respiratory ailments. These changes in air quality can have a cumulative affect on global climate change. The increase in temperatures is due to more sun hitting the Earth's surfaces.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices Into Your Daily Life To Fight Climate Change
It is possible to integrate sustainable practices into every day life by reducing the amount of resources you consume, such as food and energy. Don't buy new items every single day. Instead, shop secondhand. Additionally, eating vegetarian meals once or twice a week can help reduce the amount of methane released into the atmosphere from livestock production. Turn off lights whenever you are leaving a room in order to conserve energy.
You can also reduce the emissions from transportation sources such as cars, planes and trucks by using carpooling and public transit to transport your passengers instead of driving. Renewable power sources, such as solar panels, can be used to replace traditional fossil fuels. To make climate change action effective, it is important to support policies that promote clean air regulations. In conclusion, it is extremely beneficial to work with others on issues like ending plastic pollution or deforestation. It creates more citizens who are aware and will act upon that knowledge.