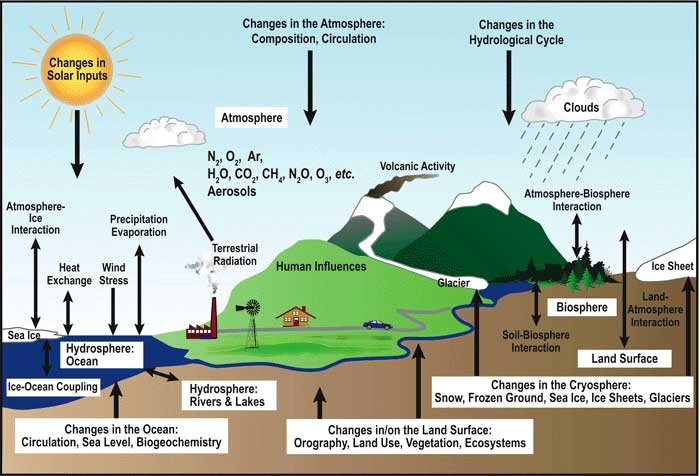
When it comes to climate change, the European public is concerned about a variety of issues. They cover everything from environmental damage to personal impacts. There is a strong perception that the world has become warmer, with an increase in extreme weather events. Despite these difficulties, the European Union made commitments to decarbonize the planet and pledged to achieve its 2050 target. The region still faces challenges in a rapidly evolving global policy environment. Europe is particularly vulnerable to the worst effects climate change has on it.
Many countries in the region are expected to be affected by climate change. Germany is one example of a country that has high levels of concern about climate change. Moreover, the country produces the second-largest coal in the European Union behind Poland. The country has struggled to reduce its coal production.
The EU biodiversity plan is an important component of the European Green Deal. This agreement aims to reduce greenhouse gas emission and decarbonize the environment. It also calls for a 50% drop in pesticide use by 2030. It also requires the restoration of 25,000 kilometers of rivers and Old-growth forests.
Young adults, especially those between 18 and 29, are more concerned with the personal effects of climate change than older adults. This is especially true for Sweden. At least 40% of young Swedes are very concerned about the potential harm from climate change.
Protests against climate change are being led by young people. Greta Thunberg, a Swedish youth climate activist is a major force in Europe. Sweden has a higher proportion of adults worried about climate change than other countries.
Young adults are also more concerned about climate change's impact on global ecosystems. They are also more likely be to adjust their lifestyles to deal with the problem. The United States also has a large gap between the ages of older and younger Americans, with the oldest being more concerned about global climate change than those who are younger.

Recent studies have shown that EU citizens are more concerned about climate change. Nearly every country in the EU that has trend data has seen a substantial increase in the number very concerned citizens. Australia, Japan (and Spain) are among the countries with double-digit increases of concern.
The most severely affected countries in Europe by climate change will be the poorest. These countries are frequently the first to suffer from extreme weather events like drought, floods or heatwaves. Moreover, the increased frequency of such events may increase the severity of diseases in humans and animals.
The European Union has set aside 25% of its budget for fighting climate change. The budget will be used to support nature-based solutions, and restore biodiversity. A biodiversity strategy has been launched by the European Commission as part of the climate mitigation strategy. This strategy, among other things, calls for the restoration or a half-off of pesticides and the restoration of 25,000km of rivers.
FAQ
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Because of the increase in average surface temperatures from human activity, the number of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes and cyclones has been increasing steadily over time. As temperatures continue to rise, this trend is likely to continue.
Global climate change can have a wide range of effects, including rising food security and displacement caused by extreme weather or sea-level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also exacerbating existing social inequalities by disproportionately affecting marginalized communities that do not possess the resources or knowledge necessary for adapting effectively.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
What are the international efforts currently being made to address climate change
The international effort to tackle climate change has reached a new level of unity and momentum. Countries all around the globe are increasingly joining forces to find solutions to climate change.
The Paris Agreement, which has galvanized global action and provides a framework for countries to establish voluntary targets to reduce their emissions, serves as a framework. In addition, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change provides political guidance as well as piloting new initiatives such carbon market mechanisms.
Progress is also being made in specific regions; for example, The European Green Deal is a comprehensive package of legislation aimed at recreating Europe's economy with sustainability at its core, while countries of the African continent have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative which aims to increase Africa's share of global renewable energy production.
Along with policy changes, action can be observed across all sectors and industries. Cities are actively moving toward sustainable public transport systems. Society as a whole is moving towards more sustainable lifestyles. Companies invent technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Investors are shifting their capital away to renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. If we are to meet the Climate goals as set out by science and enshrined into international law, governments, civil society, and private sector stakeholders must all continue to build on this momentum.
Is there any potential for new technologies that address climate change?
The possibilities of new technologies for addressing this global challenge are endless. From renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal to energy storage systems like battery packs or thermal tanks, advances in applied science are making it possible for us to transition to a more sustainable future.
New methods of carbon capture and sequestration can be employed to draw down greenhouse gas levels, while enhanced agricultural practices can reduce emissions from livestock and soil degradation. Smart grid technology may also be used to boost efficiency and improve building design.
The latest synthetic biology methods allow scientists to create organisms that can use green sources of fuel like the CO2 laser as biofuels or alternative feedstocks. This could make transportation more efficient if the market moves away from petrol-powered vehicles and towards zero-emission electric cars that are powered by clean energy.
Finally, greater investment in digital technology and AI can help empower people across borders with greater access to data on their ecological footprint and ultimately lead to more informed choices regarding consumption habits. Ultimately, understanding our role in carbon production is paramount allowing us all to be better stewards of our planet.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Climate change and global warming have a direct impact on agriculture and food security. The changing climate can impact rainfall patterns and temperatures as well as soil moisture levels. Extreme weather is also possible. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. In turn, this could increase the cost of food production and result in a greater incidence of hunger and poor nutrition worldwide.
Rising sea levels are a threat as they could flood important agricultural land along the coast. This would lead to an increase in salinity in wetlands that support important crops. Climate change can also impact livestock production. Warm summer temperatures can reduce the fertility of animals like cows, sheep, and goats. This can cause lower milk yields and increase food insecurity within communities.
Global warming and climate change are complex issues. However, governments around the world are making efforts to reduce these effects through adaptation strategies such as climate-smart agricultural (CSA) strategic investments. This involves encouraging sustainable methods, such a crop rotation technique or the conservation of indigenous seed varieties. This helps to mitigate adverse effects from changing weather or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Global farmers must adapt to climate change in order to ensure food security. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. Effective collaboration is key to creating lasting solutions that allow for the continual adherence to international dietary guidelines concerning quality nutrition in changing climates around the world. This includes all levels of government, NGOs and local communities.
What causes climate change?
Climate change is a global phenomenon. It has been caused by an increase in greenhouse gases that are emitted from humans. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Other contributing factors to climate change are population growth, land clearance and destruction of ecosystems as well as deforestation, energy use, over-grazing and energy consumption. This decreases the amount naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Climate change can also be caused by natural forces like changes in solar radiation.
This combination of human activities results in Earth exceeding its ability to balance its energy budget. The result is an average global increase of 1° Celsius since pre-industrial days. Glaciers melt faster than they form and sea levels rise as oceans absorb most of this heat energy. Other consequences include water shortages, droughts, and extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes that are caused by heavy rainfall on saturated soils.
To protect ourselves from further damage, it is essential for us to reduce our carbon footprint and start curbing our emissions now so that we have a fighting chance against the already significant impacts of climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. You can also restore some balance in these delicate cycles of the planets that sustain us, such as reforestation.
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Temperature, precipitation and sea level changes increase pressure on already finite resources. Already fragile ecosystems are being destroyed by floods or droughts. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Extreme weather events like heatwaves or hurricanes can lead to destruction of infrastructure, displacement of people and further perpetuating economic inequality.
Long-term consequences of climate change include increased resource scarcity and poverty as well as health effects such as an increase in vector-borne diseases like malaria or dengue fever. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. To build resilience against these risks, mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions is necessary. Other measures include improved management and better access to water resources.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
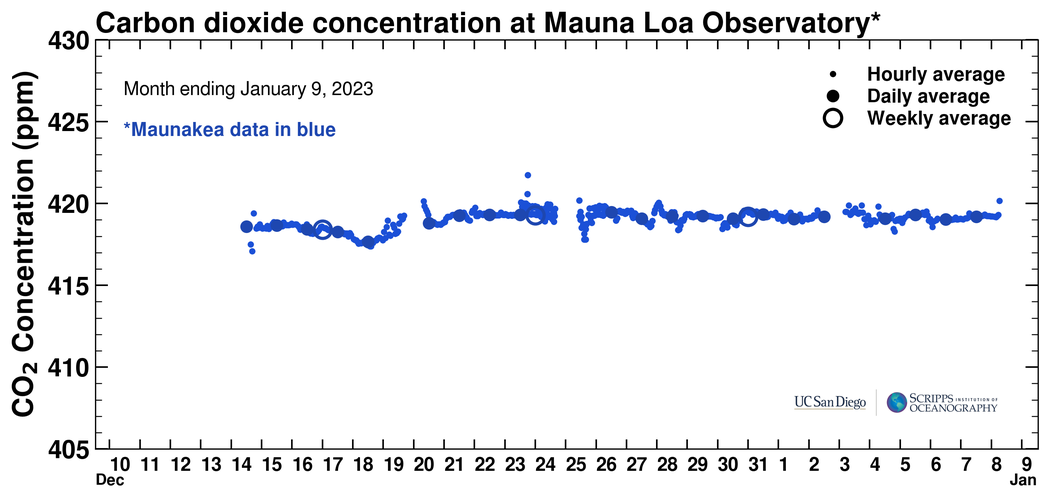
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your house more energy efficient and combat climate change
Making your home energy-efficient is one of the best ways to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on utility bills, and make life more comfortable.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. You must ensure that your windows and doors fit properly. If you find drafts around pipes or vents, make sure to add weather stripping and fill in any gaps with caulking around door frames and window frames.
Insulate your walls, ceilings, and floors to maximize energy efficiency. Inspect your attic for any air leaks or areas that aren't well-insulated.
Lighting is responsible for 18% of household electricity use. LED bulbs are up to 80% more efficient than traditional incandescent light bulbs. You can also save money by installing motion sensors and timers to turn off lights when they are not needed.
A newer model is more efficient and can help reduce your energy bills. A programmable thermostat allows you to control the temperature based on who is home and who is away.
You can replace all your windows with double-glazed windows that offer better insulation and heat resistance. Look into buying low-flow showerheads which reduce water consumption while maintaining adequate pressure levels.
ENERGY STAR rated devices use 50 % less energy than non-certified appliances. Do not forget to unplug electronic devices, such TV boxes or phone chargers, when not in usage. This can help you save considerable energy.
These few simple steps will make your home more energy efficient and reduce your carbon footprint.