A new report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has provided a detailed description of the impacts of climate change on the planet. The report found that global temperatures must remain below 1.5 degrees Celsius (C) in order to avoid serious consequences.
Five major risks are identified by the report. These are heat and drought, coastal flooding as well storm surges and sea-level rise. Below is the "burning firecrackers" chart which shows the severity of risks at various levels. Darker colors indicate greater stress levels.

Not only are there physical effects, but also socioeconomic ones. Increased flood risk and storm surges from tropical cyclones will lead to more people being forced to flee their homes. This will increase the number of deaths due to climate extreme events. The report revealed that by 2050, there will be a half a million more people living in coastal climate danger zones.
Many of the consequences of climate change are already evident, however, the report states that these impacts are greater than previously estimated. Many species have had the necessity to move their ranges in order to survive. Around half of land animals, and half of plants, have done so.
In addition to changing the ecosystems, climate change has also caused severe impacts on access to food and water. Millions are now facing acute food insecurity. Additionally, increasing temperatures and storminess are reducing the availability of water resources. A number of natural disasters have also caused more than 8,000,000 people to be evacuated around the globe.
Nearly eight percent are at extremely high risk of extinction. This number will rise to 13 % at three degrees, and to 15% at four. A higher chance of regional extinctions also exists.

Flooding will become more severe due to rising sea levels. Major cities could run out of water. The oceans are also warming, which can lead to hypoxia. This will make marine microbes less capable of absorbing oxygen. Further, more greenhouse gases will be released into the atmosphere by the melting Arctic permafrost.
Another threat to agriculture is the possibility of drought. At two degrees, agricultural drought is projected to be 150 to 200% more likely. Agricultural yields are also expected to decrease by 5 to 10 percent. The amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere could affect how zinc and other vital nutrients are affected.
Other impacts of climate change include changes in the amount of iron, protein, zinc and other nutrients. According to research, a carbon equivalent increase in atmospheric CO2 could reduce zinc by 7%. A CO2 equivalent increase in protein will also lower it by 4%.
These results are based in part on climate data derived from five global climate models. They are compared with two scenarios of emission: a low scenario, and a high scenario. Each scenario outlines a different way to reach macro-level conditions in 2030.
FAQ
What are the impact of deforestation and land use change on climate change?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. The trees that have been cut down or burned can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of Earth's most important greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide is therefore less removed from the atmosphere when trees are deforested or burned for agricultural purposes.
However, land use changes can increase greenhouse gas emissions. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. Smoke from deforestation-related burning events has been shown to cause decreased visibility and health problems such as asthma, as well as other respiratory conditions. These changes in air quality can have a cumulative affect on global climate change. The increase in temperatures is due to more sun hitting the Earth's surfaces.
In conclusion, deforestation and land-use change have resulted in a significant contribution to increased levels of global greenhouse gas emissions and have had negative impacts on local air quality that further contribute to climate change. If serious efforts to mitigate climate change are to be made, it is important that these practices are reduced.
How does climate change affect extreme weather events?
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Atmospheric temperatures have increased due to global warming which has affected different weather phenomena on a global scale.
According to climate scientists in 1980, extreme weather-related natural disasters have increased by more than twice the rate. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
Warm water was pushed towards South America by the 2015 El Nino event. This caused rising temperatures to alarming levels. Heavy rains also caused flooding in Peru and Bolivia, causing displacement and property damage. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example of climate change at work is Hurricane Irma. It was a major storm that struck Florida in 2017, causing economic losses of $50 billion.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) concluded, "Human activities are increasing the severity current climate change." This naturally leads worldwide to more severe, intense, and frequent natural disasters. There is strong evidence of humans' involvement with extreme weather events occurring frequently around us all.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change refers back to the long-term shifts occurring in global weather patterns as a result of an increase in greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat and cause global temperatures to rise, which can lead to a variety of changes in weather patterns and climate. This can include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, extreme storms and droughts, widespread coral reef bleaching, species extinction, and disruptions to food production.
Human activity is the main factor in climate change. This includes burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and transport, cutting down forests and raising livestock. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
The deforestation plays an important role in contributing approximately 15-20% to global greenhouse gas emissions. The atmosphere is effected by the carbon dioxide stored in trees when they are cut down or burned. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
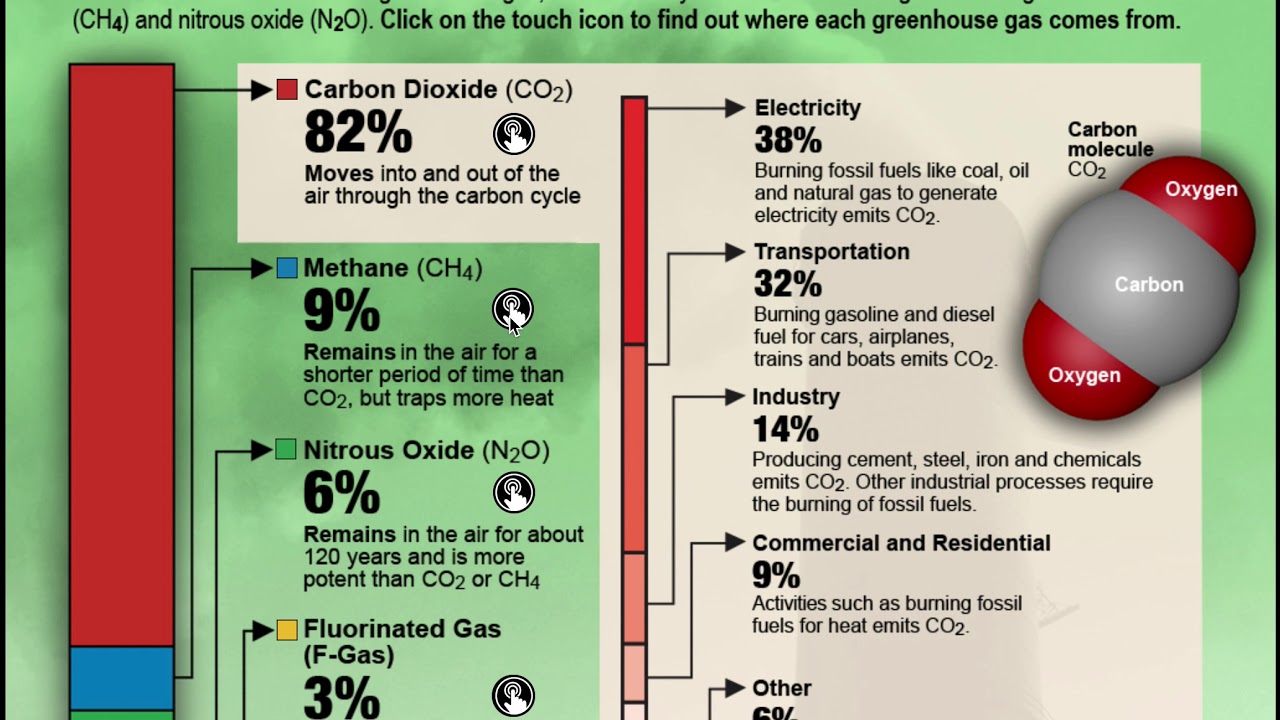
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
To reduce climate change, humanity must unite efforts across the political, social, and economic systems to reduce emissions dramatically and move away from our dependency on fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power or low-carbon hydrocarbon fuels. It could be possible to reduce atmospheric pollution by replacing polluting fossil fuels using smart solutions that encourage zero waste living. Our environmental impacts can be reduced by adopting preservation measures like reforestation. These projects help to preserve biodiversity and absorb large amounts CO2 from the environment. This helps in addressing climate change and restoring balance for future generation.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest In Clean Energy and Support the Transition To A Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is a form of renewable energy that does not produce pollution or emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such a solar photovoltaic (Solar Photovoltaic), wind power, hydroelectricity and geothermal energy. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Clean energy investors support innovation that reduces harmful emissions from electricity generation. This investment may also lead to increased economic development by creating jobs related to the production of renewable energy systems that require skilled labor and engineers. Lastly, investing in clean energy can bring investors a financial return through tax incentives programs that encourage investments into green technologies, such as wind farms, solar panels, or biomass heat generation systems.
We can both support the transition from low-carbon to a low carbon future by investing in companies that are focused on producing electricity from renewable resources like sun, wind, water and avoid activities that may harm the environment.