
In recent years the term "climate at risk" has been defined as the threat of global warming to humankind. The term was also used to encourage aggressive climate change mitigation. But the climate crisis is not just about climate change. It is also about how people respond to that change and what they do with it. This has a significant psychological impact.
Climate in Crisis examines climate change and its effects on communities, people, and the environment. It examines the effects of climate change upon Indigenous communities.
As climate change entails more extreme weather events, many environmental activists are speaking out against its impact. Some of these people are scientists and activists. Others are farmers that are starting to adopt more sustainable practices.

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change states that the climate of Earth is changing rapidly. And if we don't act, we could see an increase in extreme heat, heavy precipitation, and drought. Even the ocean levels on our planet are rising. These changes can't be reversed.
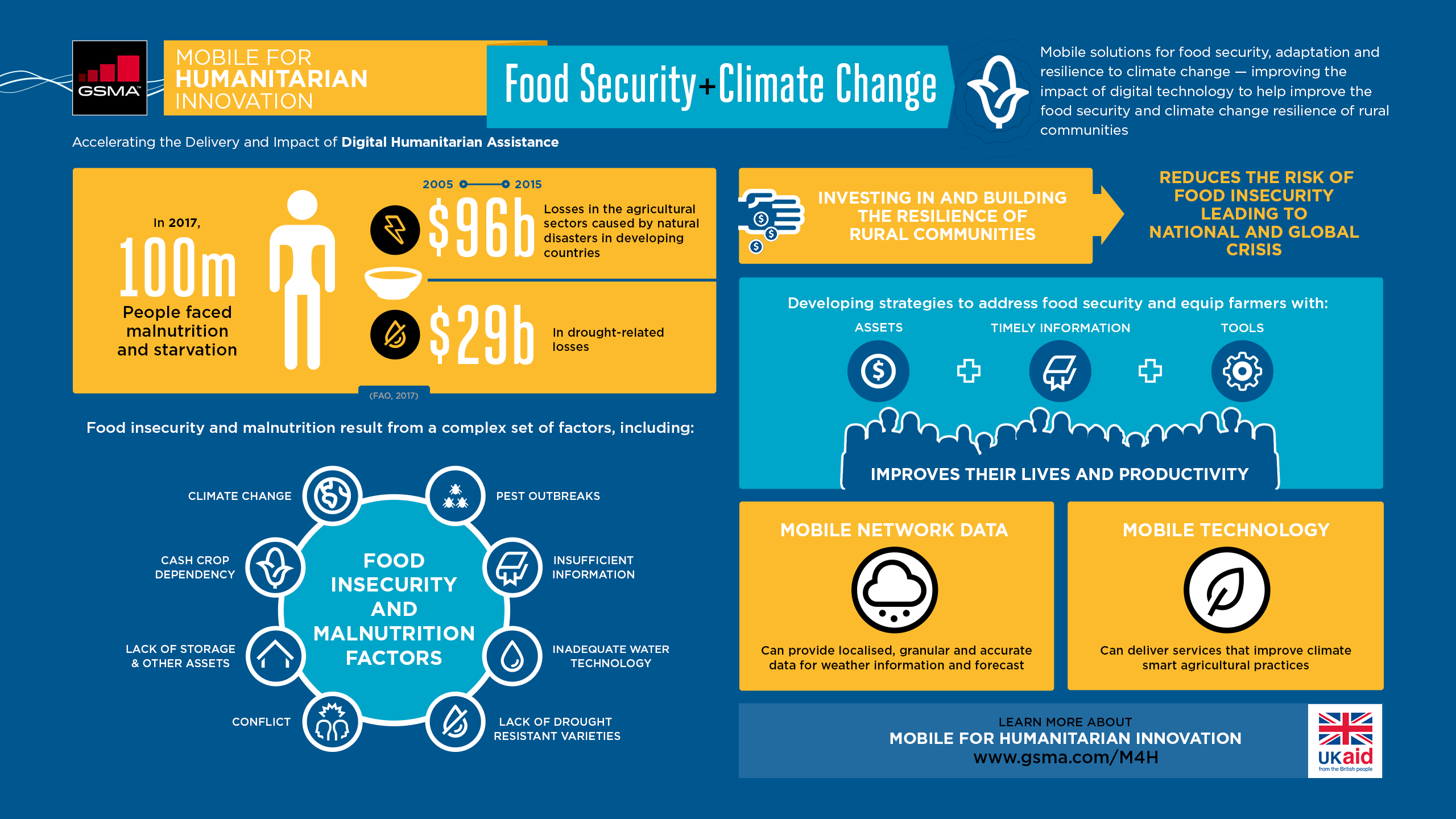
Among the most vulnerable groups to the effects of climate change are rural and nomadic pastoralists. In the Northern Triangle of Central America, El Salvador, Guatemala and Honduras (Mexico), floods and droughts have been on the rise in recent years. These conditions have affected rural economies and caused floods. Without adequate action on emissions, 75,000 people in Kenya may face riverine flooding in 2030.
Many experts predict that climate change will lead to an increase of suicide, substance abuse, mental illness, and other problems. The ACA Climate Change Task Force reported that people living in disadvantaged areas are more likely to be affected by climate change trauma.
Climate in Crisis also examines how environmental colonialism impacts Indigenous people. For example, Indigenous communities in Panama have had to cope both with deforestation logging and migration from ancestral homelands.
In Costa Rica, the country's urban development has been accompanied by concern for conservation and sustainability. Many environmental advocates feel that the media hasn’t done a good enough job of raising awareness about this issue. However, there are a number of ways that the media can improve their communications about the climate issue.
Researchers from the Political Psychology Research Group studied several Americans in an effort to understand the significance of the climate crisis. The majority of Americans believe the Earth's climate has been warming. The majority also believed it was a serious problem. However, almost half the respondents doubted that the warming was caused by human activity.
However, the majority of respondents maintained their belief that climate change is real and caused by human activity. The public's view on climate has not changed, even though the political debate has moved. There are still many technological gaps to resolve the climate crisis.
In certain cases, the false balance might sneak into the story via soundbites or a failure to analyse. The majority of issues are split 50-50.
FAQ
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented levels in atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing global temperatures to rise significantly. This can lead to droughts and heat waves as well changing rainfall patterns, melting Polar ice caps, ocean acidification and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. These changes are also threatening billions of lives and livelihoods, especially those living in areas of resource scarcity or poverty.
Due to the higher average surface temperatures due to human activity, extreme weather events like hurricanes, cyclones and wildfires have been steadily increasing over time. As temperatures continue to rise, this trend is likely to continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Climate change has been significantly affecting the world's oceans and the associated marine life since its onset. The depletion of the ozone layer, which causes constant oceanic warming, has caused major disruptions to marine ecosystems. This has led to coral bleaching and a decline in species.
Climate change is also responsible for unpredictable weather patterns and stronger storms, which can lead to dangerously high sea levels. Furthermore, changes in temperature may reduce oxygen levels in water systems resulting in "dead zones" where abundant marine life becomes sparse.
Ocean acidification is also being caused by excessive carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Ocean acidification causes an increase in pH which affects the vital functions of animals such as crabs, clams, and oysters that cannot adapt to changing conditions.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. An increase in ocean stress can accelerate already high extinction rates of many species around the world, resulting in a severe imbalance between predators/prey that could eventually lead to total extinction.
The ripple effect of climate change affects entire ecosystems. It can directly or indirectly impact multiple species through evaporation, lower water volumes, and sharp temperature shifts. Global climate change continues to decimate entire species, changing future lives on earth and below the surface of the oceans.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. You can mitigate the effects of climate change at all levels by reducing global warming trends. Further, future damages can be prevented with good management practices.
What is the climate impact of land use and deforestation?
The climate can be directly affected by deforestation and changes in land use. When trees are cut down or burned, they can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of the most important greenhouse gases on Earth. Deforestation and burning of trees for agricultural purposes removes less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Changes in land use can release more greenhouse gases into our atmosphere. For example, when forests are replaced with agricultural lands for livestock production, fertilizer, and pesticide use may increase emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
Deforestation and changes in land use have contributed significantly to the increase in global greenhouse gas emissions. They also have had adverse effects on local air quality, which further contributes to climate change. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Extreme weather events such as hurricanes or heatwaves may cause damage to infrastructure and the displacement of people. This can further perpetuate economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
What is the state of international efforts for climate change mitigation?
The current state of international efforts to address climate change is one of unprecedented unity and momentum. Countries all around the globe are increasingly joining forces to find solutions to climate change.
The Paris Agreement has been a catalyst for global action. Individual countries can set voluntary targets for reducing their carbon emissions by using the framework provided by the Paris Agreement. In addition, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change provides political guidance as well as piloting new initiatives such carbon market mechanisms.
Progress is also being made in specific regions; for example, The European Green Deal is a comprehensive package of legislation aimed at recreating Europe's economy with sustainability at its core, while countries of the African continent have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative which aims to increase Africa's share of global renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
The OECD committee's wealthy members have adopted common standards in reporting on national actions related to climate change. These are the Common Reporting Frameworks (CFR), also known as the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts demonstrate the importance of climate action. Governments, civil society & private sector stakeholders alike must continue to build upon the momentum and push towards even greater ambition & progress if there is any hope of meeting Climate goals set by science & enshrined in international law.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint & Fight Climate Change
There are many actions you can take in order to reduce your carbon emissions and fight climate change. First, you can reduce your energy consumption by purchasing energy-efficient appliances, lighting and insulation. You can also save electricity by unplugging electronics when they are not being used, using public transit, walking and turning down the thermostat in the summer and winter.
Second, try to recycle and compost all food scraps. It will help prevent them from ending up in landfills that emit methane gas. Third, plant trees around your home for shade and natural cooling since vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Additionally, look into purchasing products with minimal packaging.
You can help reduce your personal emissions by supporting organizations such as Emissions Reduction Alberta, Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute and The Nature Conservancy Canada. These organizations work to lower emissions through clean energy investments. They also support international initiatives such ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability's Urban Sustainability Strategies program.
Everyday changes can be made to help fight climate change.