
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have fluctuated between 180 - 300 parts per Million over the past 800,000 years. This level is unprecedented and will continue to rise. But this is only one difference. There are many processes that can affect climate.
Recent research shows that carbon dioxide levels in the early days of life were less than 10 times as high as they are today. They may have been around 50 million year ago. They were much warmer than today's levels of CO2 and not too far from the current levels.
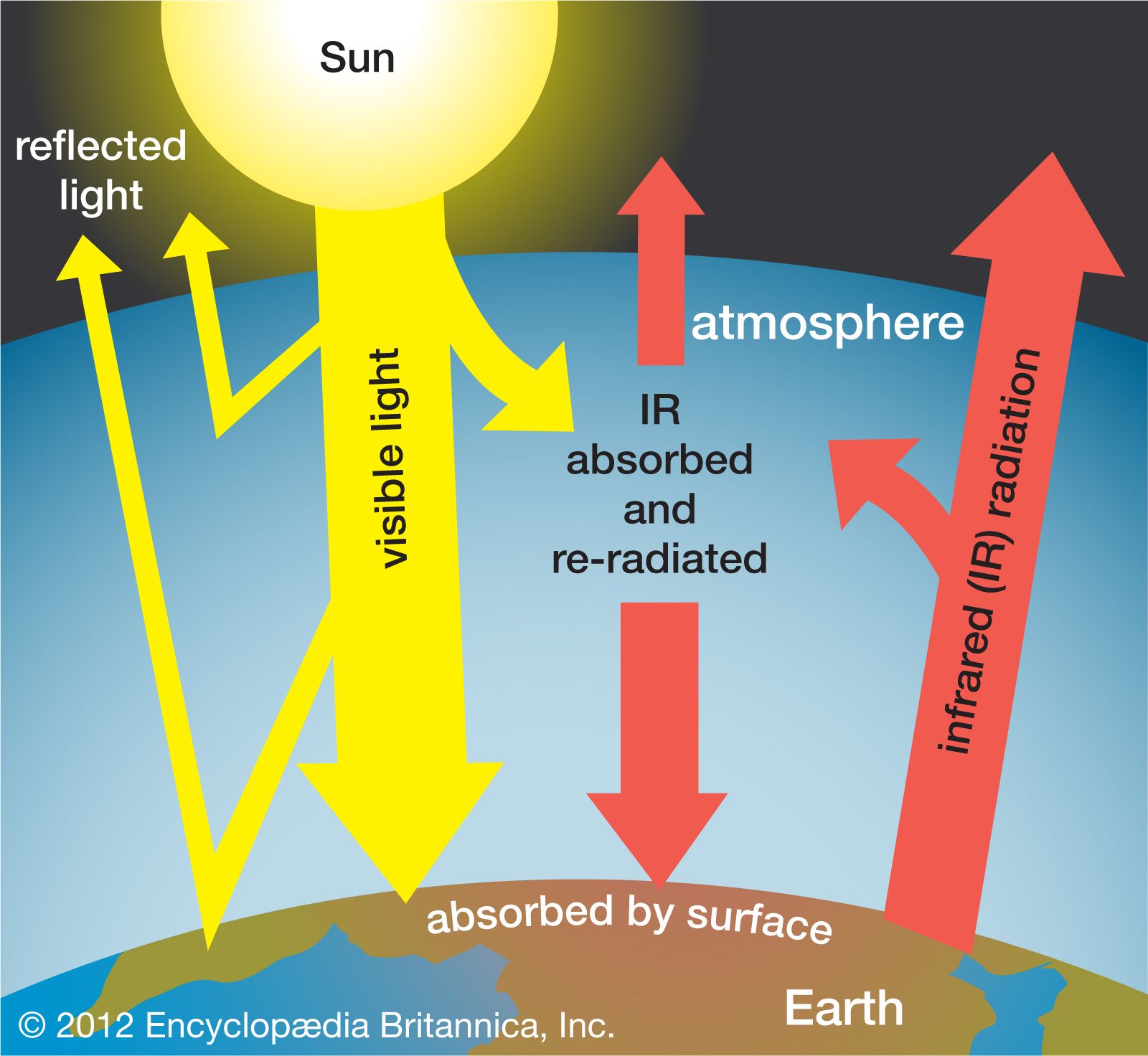
While it is clear that CO2 is a potent greenhouse gas, it is important to note that temperature is also a primary factor. For over a century, scientists have been studying the Earth's atmosphere. In fact, over 800,000 years, we know the composition. The relationship between temperature and CO2 is still not fully understood. This research team has now developed a new chemical technique that can be used to estimate CO2 levels in the distant past.
The technique involves determining how much boron is in the shells and bones of old single-celled marine algae. Tripati's team compared the rates of boron, calcium, and over 1,000 years to determine the amount carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere was around 280 parts/million at the time.
Tripati's group is working to push back the record for 20 million more years. They hope to be able estimate carbon dioxide levels for the entire time period. If this method is successful, we could finally understand the role of CO2 in global warming.
These data can be used to integrate with Earth system models for a more complete understanding of carbon dioxide exchange with the atmosphere. Data assimilation blends model simulations with actual measurements for the most realistic view on the exchange of CO2 through atmosphere.
OCO-2 satellite launched in 2014 to measure atmospheric CO2 at regional scales. Before then, ground-based sensors were used to track the measurements. These methods have been widely used to track rising CO2 concentrations for decades.
As the Earth warms, CO2 levels are expected to increase, which is projected to take the average atmospheric carbon ppm to 600 parts per million by the end of the 21st century. In the same time frame, the oceans are expected to warm by 0.2C every ten years. Because it absorbs more heat from the earth than the land, oceans are a significant contributor to global warming.
Nevertheless, the US Energy Information Administration has reported that fossil fuel consumption has fallen in western nations by nearly 47% over the past two decades. This is only a small percentage of what is possible, but it is a sign that more is to come.
While the global temperature has not been rising in the past decade, the level of carbon in the atmosphere has been increasing at a rapid pace. If we don't take steps to reduce CO2 emissions, then we will continue to see an increase of carbon dioxide levels.
FAQ
What are some of the solutions proposed to climate change? How effective are they?
Climate change has become one of the most urgent issues of our time. It requires government, businesses and citizens to pay attention. Climate disruption is obvious by rising temperatures, melting polar ice, extreme weather, higher sea levels and increasing sea levels. Multiple solutions have been proposed to address this phenomenon. These solutions range from technological solutions to behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: There are many technological solutions that can be used to combat climate change. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power provide reliable, clean energy that has minimal environmental side effects. Electric cars using renewable energy are a great alternative to petrol vehicles. They can reduce urban air pollution significantly. Other technological solutions include projects to increase carbon sequestration within trees and soil, as well coastal protection systems that protect vulnerable places from rising oceans.
Simple behavioral changes can help reduce emissions and limit future climate disruption. For example, purchasing locally produced goods with shorter supply chains reduces emissions associated with transport costs for food. Public or active transportation can optimize the use of resources, reduce cost and pollution simultaneously. Similarly, more efficient insulation in homes can decrease dependence on gas boilers to heat homes. This will also help lower bills.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
Climate change is driven by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket surrounding the Earth, trapping the infrared radiation that warms it and keeping it from getting too hot. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
The human activity of burning fossil fuels, or other industries that generate emissions, can create greenhouse gases. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (F-gases) are also major contributors to climate change.
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It's also causing changes like more severe storms and droughts as well as melting glaciers and rising sea level.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. Reforestation and other agricultural practices can be used to absorb more CO2 from air. These actions will help reduce atmospheric concentrations in greenhouse gases and create a healthier ecosystem for all life.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Since its inception the climate change has had an impact on the world's oceans, and the marine life within them. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Climate change can also be linked to unpredictable weather and stronger storms. This can cause extreme sea level rises that can prove fatal for coastal areas. Temperature changes can also cause water levels to drop, causing "dead zones", areas where there is less marine life.
Ocean acidification can also be caused by climate change. Excess carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and accumulates in the oceans. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. Ocean stress increases already high extinction rates worldwide, creating a severe imbalance of predators and prey which might lead eventually to complete extinction.
The effects of climate change ripple throughout entire ecosystems influencing multiple species whether directly or indirectly through evaporation lowering water volumes or sharp temperature shifts jeopardizing any sustainable development for fisheries and other maritime activities. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
What is the current state of international efforts to address climate change?
The current state of international efforts to address climate change is one of unprecedented unity and momentum. Countries around the world are increasingly collaborating on ways to reduce emissions, strengthen resilience against impacts, and invest in renewable energy sources.
At the global level, the Paris Agreement has galvanized collective action and serves as a framework for individual countries to set voluntary targets for reducing emissions. In addition, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change provides political guidance as well as piloting new initiatives such carbon market mechanisms.
Also, progress is being made in particular regions. The European Green Deal is an extensive package of legislation that aims at recreating Europe’s economic system with sustainability at its core. Meanwhile, countries on the African continent have committed themselves to the African Renewable Energy Initiative. This initiative aims to increase Africa’s share of global renewable power production.
In addition to policy developments, action can be seen across sectors and industries; cities are actively transitioning toward sustainable public transport systems while society as a whole is embracing more sustainable lifestyles; companies are innovating technologies that drive down emissions while investors are reallocating their capital away from fossil fuels towards renewables.
The OECD committee represents wealthy countries and has established common standards for reporting national climate action through the Common Reporting Framework, also called the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts all signify an unprecedented importance placed on climate action. For any chance of reaching the climate goals set forth by science and international law, government, civil society, & private sector actors must build upon this momentum.
What is climate change? How does it happen?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat which causes global temperatures to rise. This can cause a wide range of changes in weather conditions and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
The deforestation plays an important role in contributing approximately 15-20% to global greenhouse gas emissions. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Additionally, forests act as a natural carbon sink that removes CO2 from the air; without this absorptive capacity, carbon dioxide levels will continue to rise with devastating consequences for ecosystems around the world.
In addition to releasing CO2 into the atmosphere, human-caused pollution also emits other harmful gasses such as methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). Methane has been extensively used in industrial processes and contributes greatly to atmospheric warming. Meanwhile, N2O is emitted most commonly from agricultural soil management activities. For example, fertilization or tilling can release excess nitrogen into soil which results in N2O production upon contact with microbial organisms.
Humanity must work together across all levels of society, economy, and politics to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We need to shift from dependence on fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and low-carbon hydrogen fuels in order to limit climate change. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
What are the causes and consequences of climate change?
Climate change is a worldwide phenomenon caused by an increase of human-generated greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere. This is mainly due to fossil fuel burning for power and transportation. These emissions trap more sun's heat, causing global temperature rises.
Climate change is also caused by other factors, such as population growth and land clearing. This decreases the amount naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Climate change can also be caused by natural forces like changes in solar radiation.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. Glaciers melt faster than they form and sea levels rise as oceans absorb most of this heat energy. Other adverse consequences include water shortages and droughts as well as extreme weather events, such as flooding and hurricanes, which are often caused by heavy rains on soils.
To avoid further damage, it is crucial that we reduce carbon emissions and take steps to curb our emissions. This will give us a fighting chance against climate change's already serious impacts. It is crucial to reduce our dependence of fossil fuels for electricity generation and invest in renewable sources, such as wind turbines/solar panels. These do not emit any harmful chemicals into the environment. Reforestation and other sustainable practices can help restore balance to these delicate planetary cycles that we depend on for our survival.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy refers to any type of renewable energy that does no polluting or emit carbon dioxide, as well as other greenhouse gases. It encompasses technologies like solar photovoltaics and wind power. Investing in clean energy sources can bring many environmental advantages, including a reduced reliance on fossil resources, less air pollution, better electrical access, and greater reliability to remote locations.
Shares in companies developing innovative technologies in clean energy can be purchased by investors. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investment is a way to support innovation and reduce harmful emissions. This investment could lead to greater economic development as it may create jobs in the field of producing renewable energy systems, which require engineers and skilled labor. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
We can make a difference by investing in companies which create cleaner electricity from renewable resources, such as sun, winds, and water. While we are avoiding harmful activities to the environment, it is possible to support the transition toward a low-carbon future.